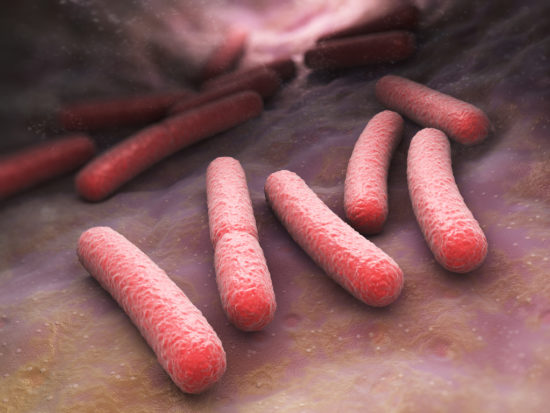
Increase in antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli in food animals between 1980 and 2018 assessed using genomes from public databases
Next-generation sequencing has considerably increased the number of genomes available in the public domain. However, efforts to use these genomes for surveillance of antimicrobial resistance have thus far been limited and geographically heterogeneous. We inferred global resistance trends in Escherichia coli in food animals using genomes from public databases.
Our analysis illustrates the potential of using the growing volume of genomes in public databases to track AMR trends globally.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!