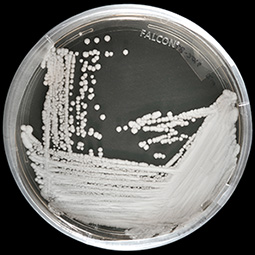
Mechanisms of Candida auris Transmission within the Healthcare Environment
The authors found high concentrations in the skin swabs of colonized residents that often exceeded 106-107 cells/mL. They then evaluated the relationship between C. auris concentrations in these skin swabs and their associated environmental samples with Kendall’s tau-b (τb) correlation, which showed a strong, positive, and statistically significant relationship for both culture-dependent (τb = 0.536, p = 0.0004) and culture-independent (τb = 0.657, p = 3.832e-6) data.
C. auris colonized patients can have very high burden on their skin. This bioburden is positively correlated with the C. auris concentrations on associated surfaces. These findings support the shedding hypothesis and provide a new perspective to focus infection control efforts
AMR NEWS
Every two weeks in your inbox
Because there should be one newsletter that brings together all One Health news related to antimicrobial resistance: AMR NEWS!