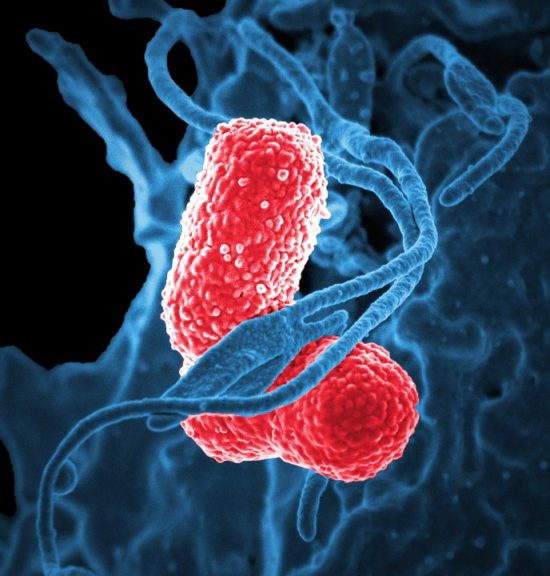
Global burden of Klebsiella pneumoniae infections and antimicrobial resistance in 2019
This study evaluates the global burden of Klebsiella pneumoniae infections and associated antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in 2019 by integrating data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 and the Global Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance 2019 study. Their modelling of 471 million records estimates around 800 000 deaths worldwide due to K. pneumoniae infections, with approximately 80 % of those attributable to resistance. The greatest mortality burden occurs in lower-respiratory-tract, bloodstream, and intra-abdominal infections (≈ 90 % of K. pneumoniae-related deaths). Regionally, South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa are most impacted, with sub-Saharan Africa having the highest rate of AMR-linked deaths; resistance to carbapenems and third-generation cephalosporins underlies over half the mortality. The authors conclude there is an urgent need for targeted interventions in high-burden regions to address both the infections and the AMR component.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!